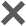
Chinese wine culture has a long history and a wide variety of wines. Especially in the Spring Festival, the grandest and most important festival, wine is of course an indispensable element. Wine is a wonderful thing. We can directly experience the emotional and physical changes it causes, but what's going on in our bodies.
01. What is alcohol
Alcohol, also known as ethanol, is made by fermentation of carbohydrates.
There are many varieties because of the different ingredients used and the way they are brewed.
02. How Alcohol Is Metabolized
Alcohol is metabolized very differently from the three nutrients (fat, carbohydrate, and protein).
In fact, our bodies metabolize it as a foreign body/poison.
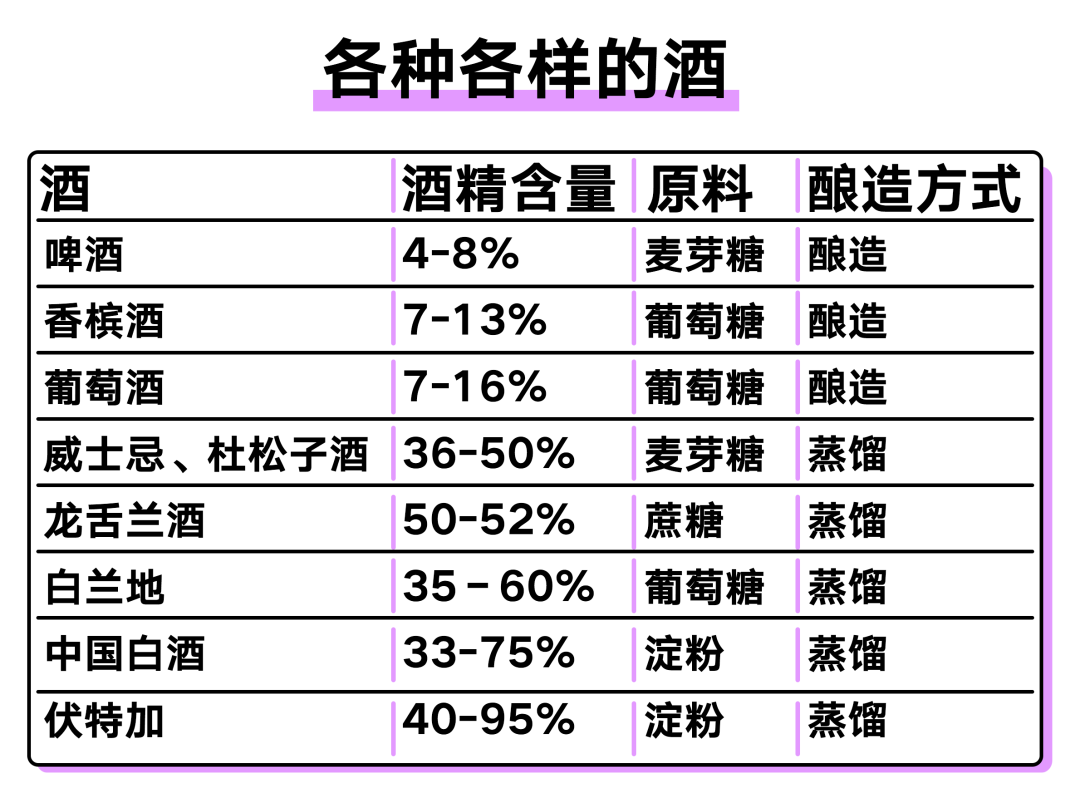
A small portion of the wine travels to the intestines. Most of it is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the portal vein, where it travels to the liver. Ninety percent of alcohol is metabolized in the liver in the following way.
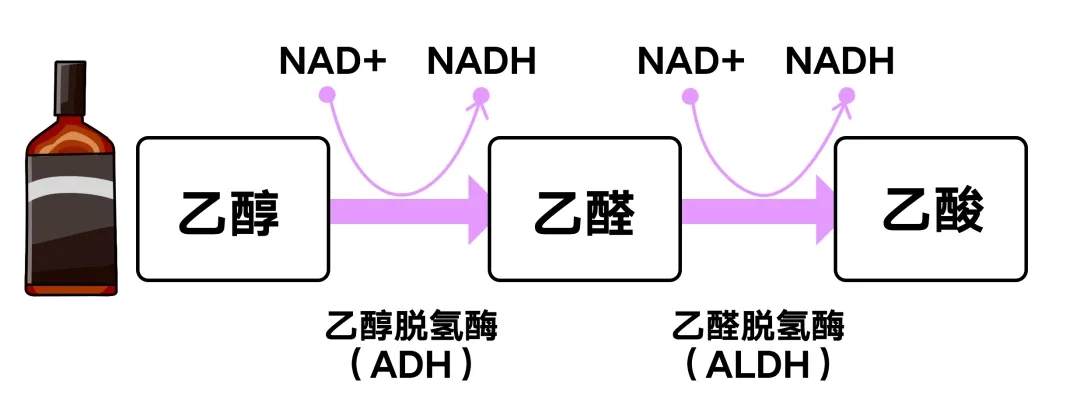
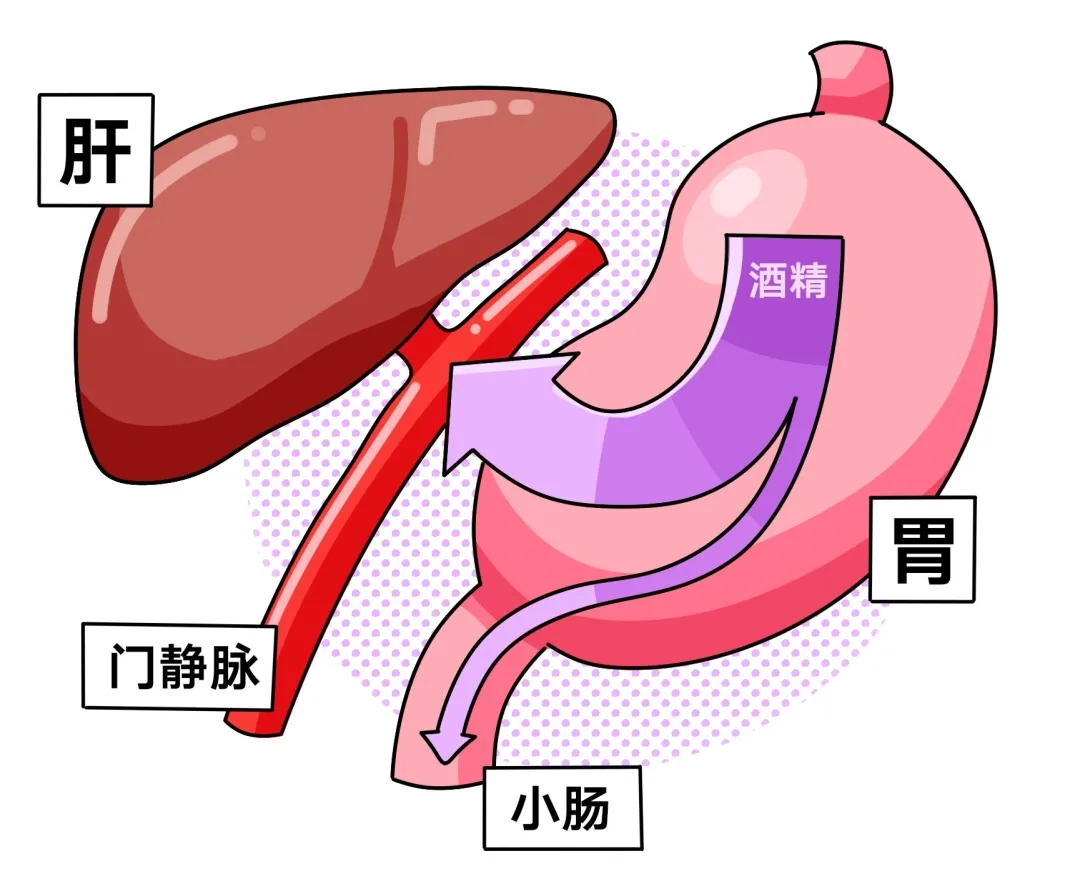
First, ethanol is oxidized to acetaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase ADH and NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
Then, acetaldehyde is oxidized to acetic acid by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH and NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
Finally, acetic acid leaves the liver and circulates to peripheral tissues, where it is metabolized into acetyl coenzymes, which are oxidized to produce carbon dioxide, fatty acids, ketone bodies, and cholesterol.
1. Acetaldehyde is a primary carcinogen
One of them, acetaldehyde, is a very toxic carcinogen that has an effect on dilating blood vessels, so it's the same substance that causes headaches and flushing after drinking. And acetaldehyde can interfere with DNA replication, damage DNA.
2. Two important enzymes that metabolize alcohol
If the alcohol dehydrogenase ADH in the body is insufficient, it will cause the accumulation of ethanol, easy to get drunk.
If the body acetaldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH is insufficient, will cause acetaldehyde accumulation. The buildup of acetaldehyde causes flushing, redness and vomiting, and increases the risk of liver damage. About a third of Asians lack the aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH to metabolize acetaldehyde. Europeans, Africans and Americans generally do not have this problem.
3. Can the drinking capacity be trained
And that has to do with these two enzymes. But unfortunately, the amount and type of these two enzymes are almost genetically determined and difficult to change after nurture. So people who flush easily with alcohol, that is, not enough ALDH, cause acetaldehyde to build up. If forced to drink more alcohol, it will only cause more acetaldehyde accumulation, which is very harmful to the body.
4. The reduction of NAD+/NADH affects other REDOX reactions
Because of the heavy use of NAD+ in the above two steps, NADH is produced. NAD+ is an important molecule in cells that provides energy for reactions. As a result, important biochemical reactions that require NAD+ are inhibited, including the oxidative decomposition of fatty acids, gluconeogenesis, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Reactions that require NADH are promoted, such as steatogenesis (alcoholic fatty liver disease). Simply put, the metabolism of other foods is forced to stop and alcohol is metabolized in priority. As a result, drinking too much alcohol can eventually cause hypoglycemia.
03. The health effects of alcohol
A 26-year trial study of 195 countries, published in 2018 by The Lancet, found: How much alcohol do we need to minimize the health risks of drinking?

The answer is 0.
It is highly unlikely that drinking alcohol will do us any good.
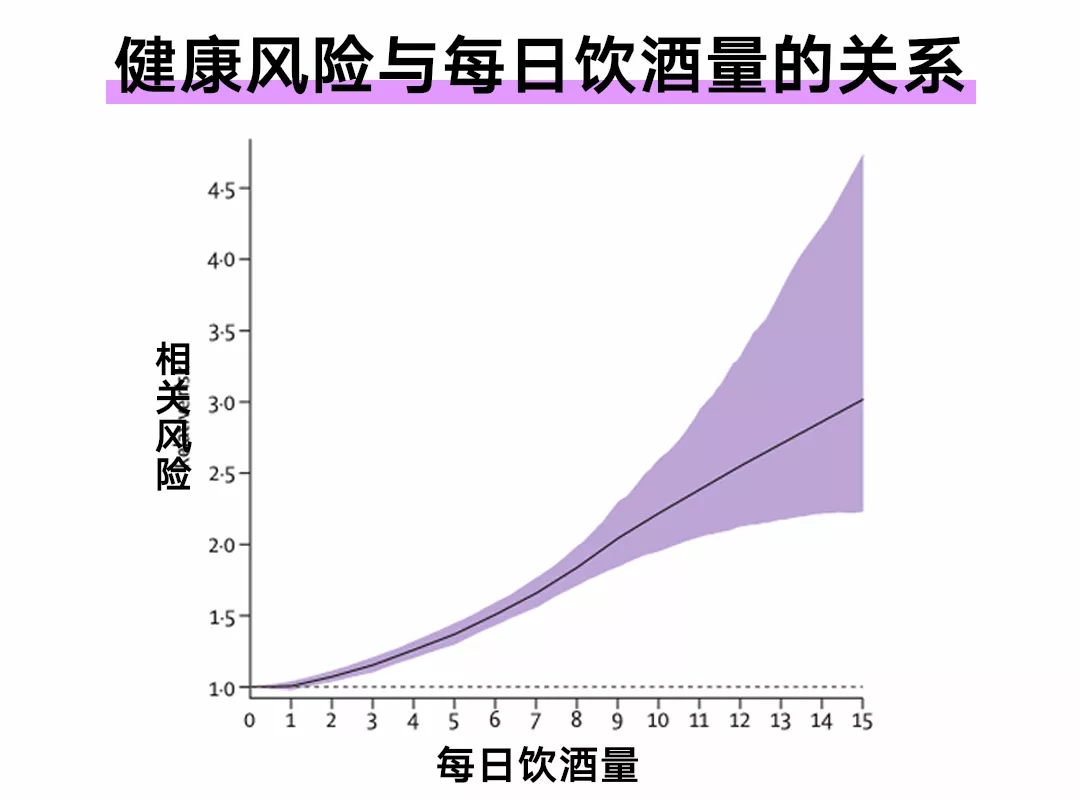
The more you drink, the greater the health risks.
Alcohol is classified as a group 1 carcinogen by the WHO, and in particular increases the risk of various cancers, including the upper respiratory tract, liver, colon or rectum, and breast.
04. Drinking and taking pills
You must have heard that eating cephalosporin can not drink, in fact, there are a lot of drugs can not drink! This is because the metabolism of these drugs affects enzymes that metabolize alcohol, which in turn interferes with the metabolism of the drug.
1. Disulfuram antibiotics: cephalosporins, metronidazole, furazolidone, toluene sulfonamide, chloropropyl sulfonamide
These drugs react with alcohol in what is known as a disulfiram-like reaction. Because the drug contains dithiulam, inhibits acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, also causes acetaldehyde accumulation poisoning. Reactions such as weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, hallucinations, general flushing, headache, nausea, vomiting, decreased blood pressure, and even shock can occur after drinking even small amounts of alcohol.
2. Antipyretic and analgesic drugs: aspirin, acetaminophen, ibuprofen, flurbiprofen, fenoprofen, ketoprofen, naproxen, dicloprofen
These drugs can speed the emptying of the stomach, causing irritation and damage to the gastrointestinal tract, as can alcohol, which increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. In addition, alcohol can affect the metabolism of acetaminophen, metabolizing it into a drug that can lead to liver damage.
3. Clotting agent: warfarin
Chronic alcohol intake can increase the metabolism of coagulant and decrease the anticoagulant effect. However, acute alcohol intake can decrease the metabolism of coagulant and increase the anticoagulant effect.
4. Diabetes hypoglycemic drugs: metformin, insulin, toluene sulfonamide, sulfonamide chloropropanuron, glipizide
These drugs promote the lowering of blood sugar, which alcohol consumption also causes by inhibiting the normal metabolic response. Medication combined with alcohol increases the risk of hypoglycemia.
5. Sedative sleeping drugs: phenobarbital, chloral hydrate, diazepam, nitroazepam, clonazepam, triazolam
Muscle relaxants: Muscle Anxin, Cyclobenzarin
Antihistamine allergy drugs: diphenhydramine, chlorpheniramine, clomastine, hydroxazine, promethazine, cyheptadine
Tricyclic antidepressants: amitriptyline, clomipramine, desimipramine, doxepine, desimipramine, desimipramine, desimipramine
Opioid drugs (pain relief) : codeine hydromorphophen, fentanyl, morphine, pethidine, propoxyfen
These drugs are central nervous system (CNS) inhibitors, have the function of inhibiting respiration, heartbeat. Alcohol accelerates the absorption of these drugs; What's more, alcohol has a stimulant effect on the central nervous system (CNS) and then inhibits it. Together, they can greatly enhance the effect of this neural inhibition, and excessive inhibition can lead to lethargy, coma and respiratory failure.
6. Antihypertensive drugs: reserpine, captopril, nifedipine
Blood pressure drugs cause vasodilation, which lowers blood pressure. Alcohol has the same effect. So taking blood pressure medicine and drinking alcohol can enhance the effect of blood pressure medicine, causing headaches and even shock. However, some antihypertensive drugs, such as combination antihypertensive tablets, combination dipyrazine and alcohol, can also cause a sharp increase in blood pressure.
7. Anticonvulsant (epilepsy) : phenytoin
Long-term alcohol use can cause phenytoin to break down, reducing its therapeutic effect and making it difficult to control the seizure.
8. Arthritis drugs: Celebrex, Futarin, Naproxen
Mixing with alcohol increases the risk of stomach ulcers and bleeding, as well as liver problems.
Therefore, it is best not to drink alcohol while taking the medication, and if you must take it, check the instructions carefully and consult your doctor.
05. Alcohol and Weight Loss
Drinking and losing weight are two contradictory things. We can analyze them from the following two aspects.
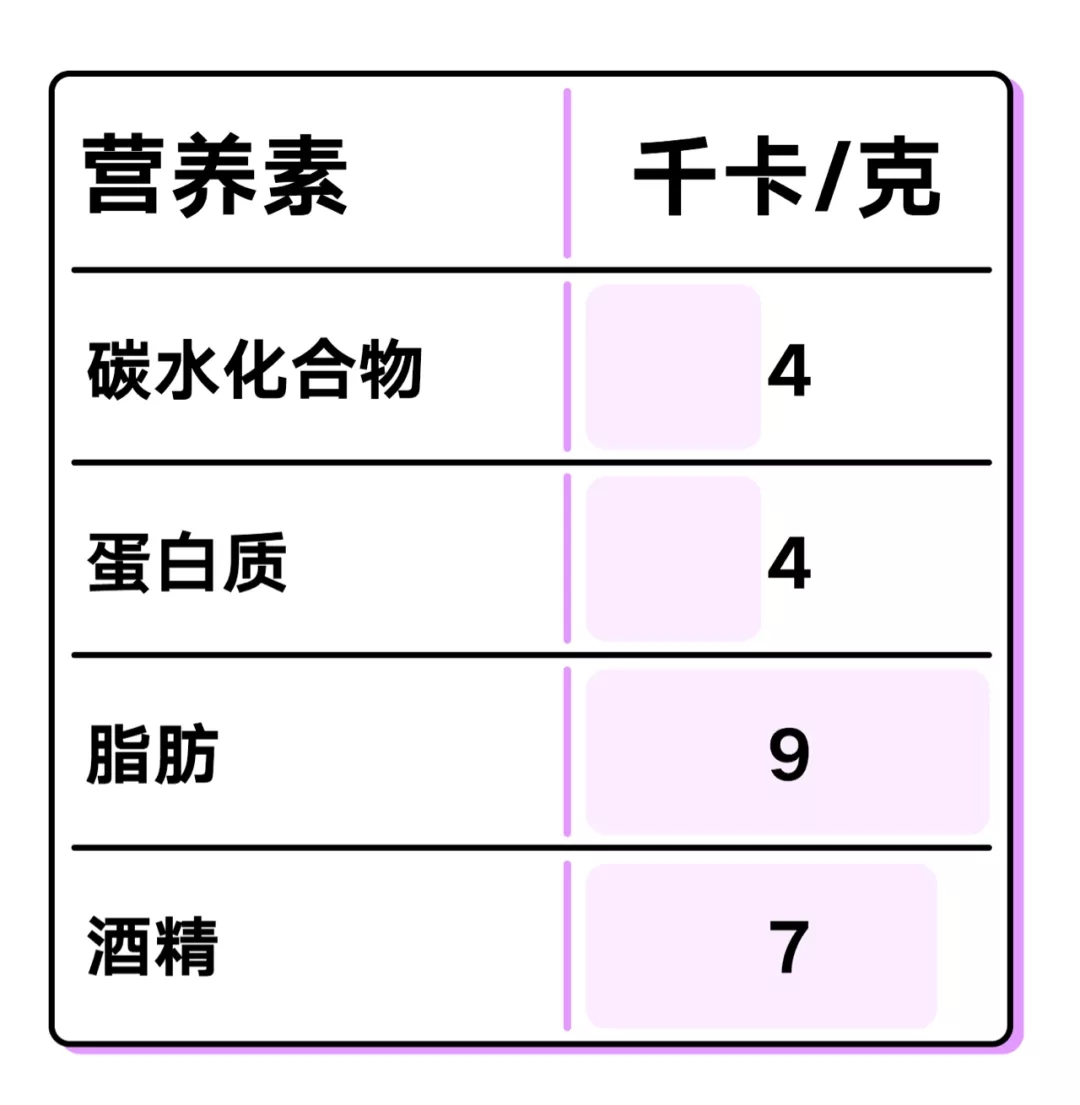
1. Calories of alcohol
Alcohol is not one of the three essential macronutrients and does not contain the vitamins and minerals needed. But it's still hot, and it's produced by acetic acid metabolism. And the calories are not low, per gram is nearly twice as much as carbon, water and protein. So this empty calorie bomb isn't exactly fat loss friendly (it all depends on the quantity, of course).
2. Alcohol affects lipodecomposition
Unlike carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, alcohol can only be stored by the body; it can only be metabolized. When alcohol is metabolized, the NAD+/NADH ratio decreases, which affects the metabolic pathways of other nutrients. Furthermore, when metabolizing alcohol, the metabolism of fat will be suspended, making it difficult to lose fat.
06. If you have to,How does low carbon give birth to ketone drink
It's clear that drinking alcohol doesn't do you any good in terms of health or fat loss. But it still has irreplaceable social properties that give us emotional value. If you're in low carb ketogenesis, you're going to care a lot about the carb and water content. We used one unit of alcohol, or about 10ml of pure alcohol, as the benchmark, which is about 1 glass of beer (250ml) and 1 glass of red wine (100ml). 1shot spirits to compare the carbohydrate content of different wines.

As you can see, cocktails, which are spirits with drinks and sweeteners, are very high in carbohydrate content, and these carbohydrates mainly come from the drinks and sweeteners.
Beer has the highest carbohydrate content among non-alcoholic drinks, with about 12g in a single drink. (Beer has a lower alcohol content and is easier to overdrink.) So if you're drinking a lot of beer you're also consuming a lot of carbs, and high carbs are very bad for cardiovascular function; In addition, beer contains more gluten, which is easy to cause inflammation.
A glass of wine and champagne contains about 2g of carbs, and typically a glass of wine doesn't have a significant effect on blood sugar or insulin levels.
Hard distilled spirits (whiskey, vodka, brandy, tequila, gin) and Chinese baijiu are highly alcoholic, with almost zero carbs in a small glass, and meet the requirements of a low carb and ketogenic diet. But don't forget the metabolic pathway of alcohol, which itself is a very toxic carcinogen.
07. The last word
Certain levels of alcohol (which vary from person to person) alter the mechanisms of dopamine, GABA and opioid nervous systems and may indeed give us a brief feeling of Euphoria, but long-term health factors still need to be considered.
This isn't about never drinking. This is about drinking more intelligently, choosing the right drink for you, or figuring out your reasons for not drinking, based on what it takes.
Spring Festival drinking remember the right amount, and do not drink on an empty stomach.
This article is reprinted from: Beast Life
Guiding Unit:
Urban and Rural Community Development Governance Committee of CPC Chengdu Municipal Committee
Education, Culture and Health Bureau of Chengdu High-tech Zone
Trade Union of Chengdu Hi-tech Zone
Sponsor:
Chengdu Hi-tech Medical Association
Undertaker:
Chengdu Hi-tech Medical Association Nutrition Sports and Health Branch
General Medicine Branch of Chengdu Hi-tech Medical Association
Chengdu Hi-tech Medical Association Institute Sense Branch
Breast disease special committee of chengdu hi-tech medical association
Heart function committee of chengdu hi-tech medical association
Co-organizer:
Beijing Huayi Network Technology Co., Ltd
Chengdu Business Daily • Sichuan famous doctor
West China Hospital of Sichuan University
West China Shangjin Fen Hospital, Sichuan University
Institute of Public Health and Social Development, Sichuan University
Tianfu International Alliance for Nutrition Sports and Health Innovation
Chengdu Pension Welfare Association
Chengdu BOE Hospital
Sichuan Modern Hospital
Chengdu Huang Zai Military Hospital
Futurecome Technology Co., Ltd
Sichuan medical team