Circle of friends, the first batch of "hit" friends have been promoted into "Yangkang".
Now, it seems, it is not time to let down our guard. A new strain is on its way.
As the country liberalizes further, we will face more uncertainty.
But what is certain is that the New Crown is the best at coming back and delivering the knockout blow when you let your guard down.
Here are some tips on COVID-19 complications and prevention for you and your family.
01 Cough and pneumonia
Cough and pneumonia are different concepts.
A cough is only a symptom of a disease, not a disease, and can be caused by many things. Coughing by itself does not cause pneumonia. Cough usually occurs when pathogens such as viruses and bacteria affect only the upper respiratory tract. When inflammation reaches the lower respiratory tract, it can develop into pneumonia. Cough is also one of the most common clinical manifestations of pneumonia.
If there is cough blood (blood in sputum), night (or change of position) cough aggravation, cough a lot of yellow pus sputum, or fever again, shortness of breath, dyspnea, chest pain and other original symptoms significantly worse, and cough for more than 2 weeks, it is recommended to go to the hospital.
To determine whether pneumonia exists, you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
General symptoms: whether there is general discomfort, fatigue, headache, anorexia or general muscle, joint pain;
Local symptoms: cough, sputum, chest tightness, shortness of breath, dyspnea and other common symptoms of pneumonia; Other symptoms: whether the patient self-perceived shortness of breath, rapid breathing rate, etc. In addition, family members can observe whether the elderly, children and other family members are different from the usual performance, such as mental burnout, shortness of breath, lips purple.
In addition, the elderly whether there is a lack of consciousness, change of consciousness or easy to feel tired, physical decline, response to slow and so on. In case of the above conditions, it is necessary to go to the hospital in time for a clear diagnosis and active treatment to avoid the delay of the condition.
02 Beware of viral myocarditis
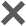
According to a video posted by a cardio-cerebrovascular doctor at Sun Yat-sen University, a 19-year-old man's fever went down and his sore throat improved a week after he contracted COVID-19, but he suffered from chest tightness and shortness of breath.
Go to the hospital to check, myocardial enzyme significantly increased, is acute myocarditis.
Numerous studies at home and abroad have found that the novel coronavirus can easily attack the heart of infected people and induce myocarditis.
A US study published in the Journal of Rehabilitation compared 150,000 veterans 30 days after infection with two groups of uninfected soldiers.
The data found 20 marked increases in cardiovascular problems in the year following infection.
Wuhan also conducted a survey in 2020, showing significant differences in heart rate and fatigue level between normal people within 60 days after recovering from COVID-19 infection.
What does it mean?
After "Yangkang", our cardiovascular system did not fully return to normal state.
Many people have Yang feel, palpitation, chest tightness, shortness of breath.
Some people are tired every day, unspeakably uncomfortable. He gasped and his heart throbbed.

Be alert if these symptoms appear within 2 or 3 weeks of infection, as myocarditis usually occurs during this time.
Chen Qizhi, a physician at the School of Medicine of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, once said that myocarditis can attack people of all ages and genders with "no difference", and young adults aged between 20 and 40 are more susceptible than the elderly and children.
Long time discomfort to timely medical treatment, do an electrocardiogram and blood test, do not be careless.

03 Beware of silent hypoxia
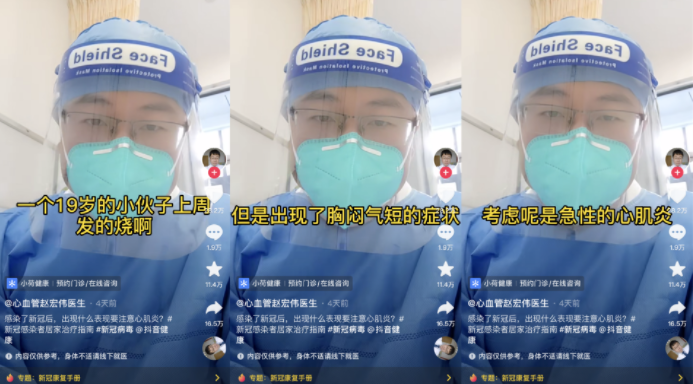
Not long ago, Fan Deng, a teacher whose father passed away due to COVID-19, mentioned in his wechat moments a problem that no one had noticed before: silent hypoxia.
What is silent hypoxia?
Lung cells are attacked by the novel coronavirus, the alveoli are reduced, oxygen intake is insufficient during respiration, and blood oxygen concentration drops.
Normal people will breathe heavily when hypoxia, there is a violent reaction, but some elderly patients to hypoxia response is very dull, even completely feel the chest tightness, breathing difficulties.
According to teacher Fan Deng, he saw his father was a little confused, so he put on a blood oxygen meter at home and measured his father's blood oxygen concentration. The self-measured blood oxygen concentration was 88%. When he sent to the hospital, the blood oxygen level had dropped to 66%, and CT showed that the old man's lungs had turned white in a large area.
No symptoms on the surface, the family is not easy to detect, the actual old man has respiratory failure, called "silent hypoxia".
"There's been a lot of that this time," he said.
Dr. Zhang stressed that there are two warning values for silent hypoxia.
The normal body oxygen saturation is between 96% and 100%, and less than 95% is hypoxic.
93% is the first warning line, when the body's organs have been deprived of oxygen.
90% is the danger line of hypoxia, when the organs are in a state of extreme hypoxia, requiring emergency medical treatment.
For patients infected with COVID-19, a blood oxygen level below 93% is considered severe.
Song Yuanlin, director of the Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine at Shanghai Zhongshan Hospital, also mentioned that although "silent hypoxia" mostly affects the elderly, it can also affect young and middle-aged people, such as desk workers for a long time, pregnant women and people who snore during sleep.
Families with conditions can prepare a fingertip oximeter to monitor the condition of the elderly at any time. If not, some sports watches also have the function of monitoring blood oxygen.
If you don't, you can also tell if your blood oxygen is dropping by looking at the following symptoms:
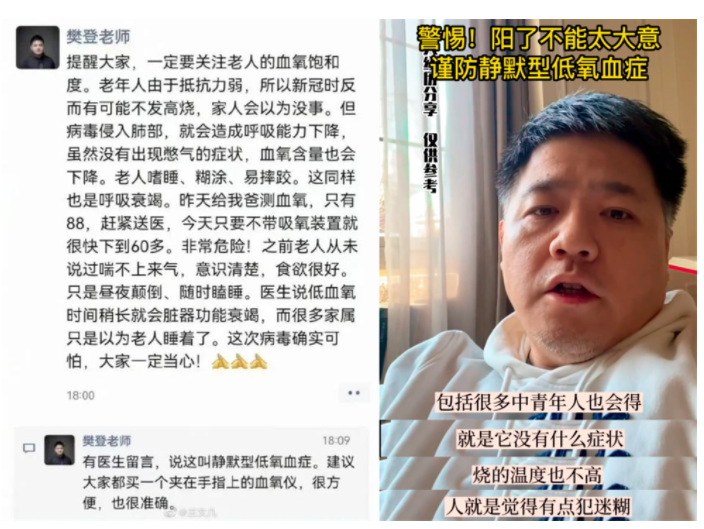
Rapid heart rate, breathing rate greater than 30 beats per minute, dry, gray hair, blue, purple lips, lethargy, unresponsive conversation, profuse sweating for no reason.
Once you have the above symptoms, you should go to the hospital for examination and evaluation as soon as possible.
04 It is recommended that Yangkang be vaccinated against COVID-19 after six months
"Although it is unlikely to be re-infected with the same COVID-19 variant in a short period of time, people with poor immunity are prone to repeated infections, including the elderly, young children, people with underlying diseases and people with immunodeficiency, and there is a risk of re-infection in a short period of time, especially in the face of new variants." Zhang Boli said, in addition, doctors, nurses and other high-risk positions in the working environment, the risk of transmission is high, contact with mutant strains, high work intensity, the risk of secondary infection is high.
"It is mainly a case of reinfection with a variant of the novel coronavirus, so we should continue to take personal precautions even if the infection turns negative." Zhang Boli, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, stressed that Yangkang can be vaccinated against COVID-19 after six months, and it is best to adopt a sequential strategy of injecting xenogeneic vaccine to strengthen the immune barrier.
For those who have recovered from COVID-19, the best way to prevent reinfection during the epidemic is to take good protective measures, including wearing masks, paying attention to hand hygiene, taking good rest, frequent ventilation, and maintaining social distancing. Especially for the elderly and children with Yang to Yin, they should keep warm, gather as little as possible, ensure good hygiene habits, pay attention to nutritious diet, and enhance immunity. Reduces the risk of reinfection.
In case of reinfection, it is important to distinguish between reinfection and reinfection. "Reyang" occurs within 2-3 weeks after the transition to Yin. Patients generally have no obvious clinical symptoms, mainly positive virus fragments detected in the body, and generally have no infectivity. However, secondary infection usually occurs within a few months to a year after the first infection, which is equivalent to a new infection. It usually has clinical symptoms and high viral nucleic acid load, which is infectious.
"Patients with 'fuyang' do not need further treatment. They need to pay attention to rest, reasonable diet and nutrition." Zhang warned that patients with secondary infections need to undergo standardized treatment again, strictly do a good job of personal protection, do a good job of self-isolation, pay attention to the protection of family and colleagues, to reduce the risk of the spread of the epidemic.